Electric bikes are now widely used for commuting, recreation, and high-performance riding. Yet many riders are still unsure what terms like Class 1, Class 2, and Class 3 really mean. Understanding ebike classes goes far beyond speed limits—it affects where you can ride, how your bike performs, and whether it truly matches your lifestyle.
This guide explains ebike classes in a practical way, helping you choose the right electric bike class based on real-world riding needs.
What Are Ebike Classes?
Ebike classes are a standardized system used to categorize electric bikes based on motor assistance type and maximum assisted speed. Rather than treating all e-bikes the same, this framework creates clarity for both riders and regulators.
From a performance perspective, ebike classes also help riders understand how an electric bike will feel on different terrain and at different speeds.
Why Ebike Classes Matter
Many riders think ebike classes only matter for legal compliance. In reality, they strongly influence acceleration, control, and overall riding confidence.
Choosing the right ebike class ensures your bike matches your commuting needs, terrain challenges, and riding expectations.
Class 1 Ebike: Pedal Assist up to 20 mph
A Class 1 ebike provides motor assistance only while pedaling and stops assisting at 20 mph. This class offers the most traditional cycling feel and is often allowed on bike paths and trails where standard bicycles are permitted.
Class 1 ebikes are well suited for casual riders, fitness-oriented cyclists, and trail systems with strict access rules.
Class 2 Ebike: Throttle-Assisted up to 20 mph
A Class 2 ebike includes a throttle, allowing the motor to power the bike without pedaling. The maximum assisted speed remains capped at 20 mph.
This class is popular for urban riding, stop-and-go traffic, and riders who value convenience and control.
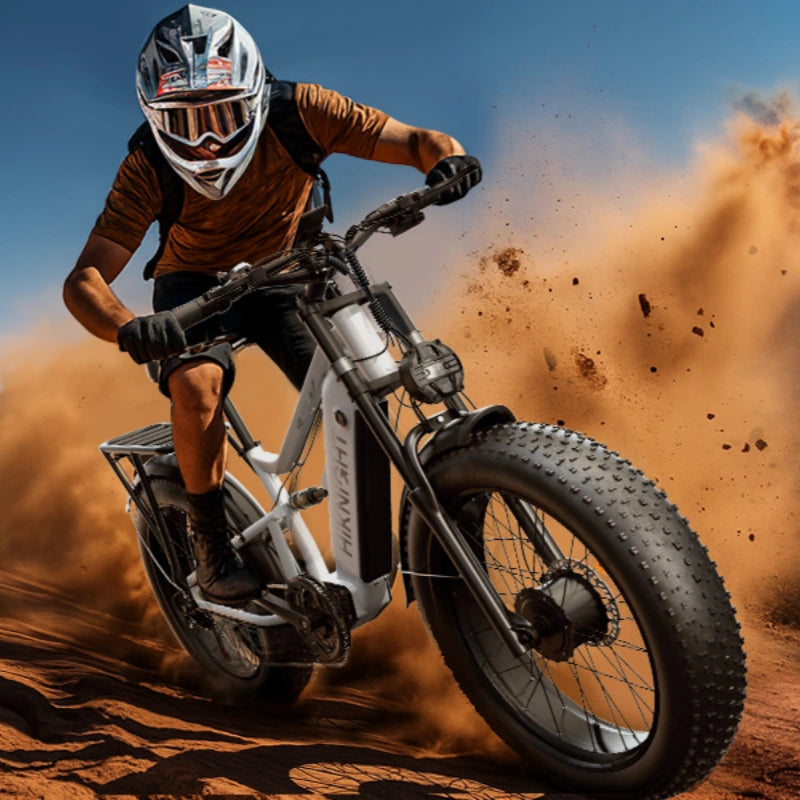
Class 3 Ebike: High-Speed Pedal Assist up to 28 mph ⚡
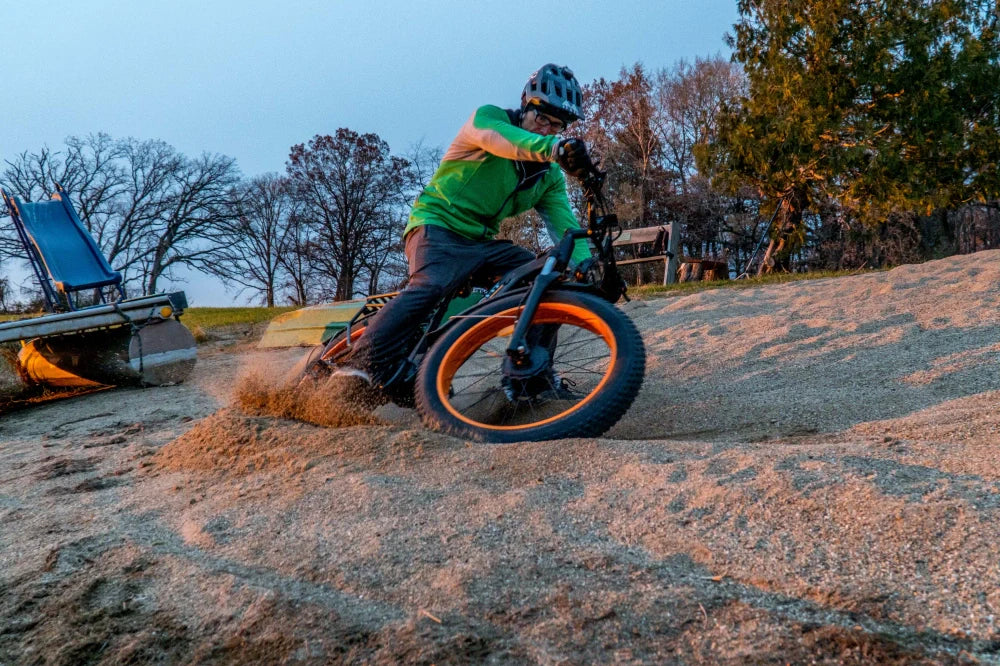
Class 3 ebikes provide pedal assistance up to 28 mph, making them the fastest category within standard ebike classes. These bikes typically feature stronger motors, upgraded braking systems, and more robust frames.
Performance-focused brands like HiKNiGHT concentrate heavily on this category. The HiKNiGHT H6 Pro dual motor off-road electric bike demonstrates how Class 3 performance supports demanding terrain, steep climbs, and high-torque riding.
Comparing Ebike Classes
When comparing ebike classes, speed alone does not tell the full story. Power delivery, terrain capability, and riding stability all play a critical role.
- Class 1: Natural ride feel with limited speed
- Class 2: Flexible control with throttle support
- Class 3: High-speed performance for serious riding
How to Choose the Right Ebike Class
The best ebike class depends on how and where you ride. Consider traffic conditions, terrain type, and whether you need throttle assistance or higher cruising speeds.
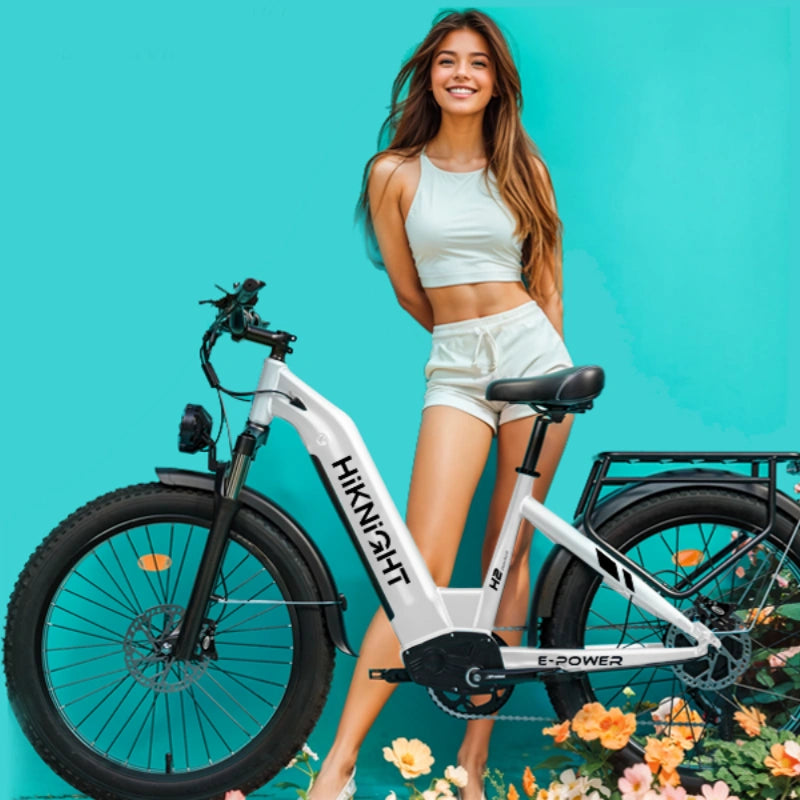
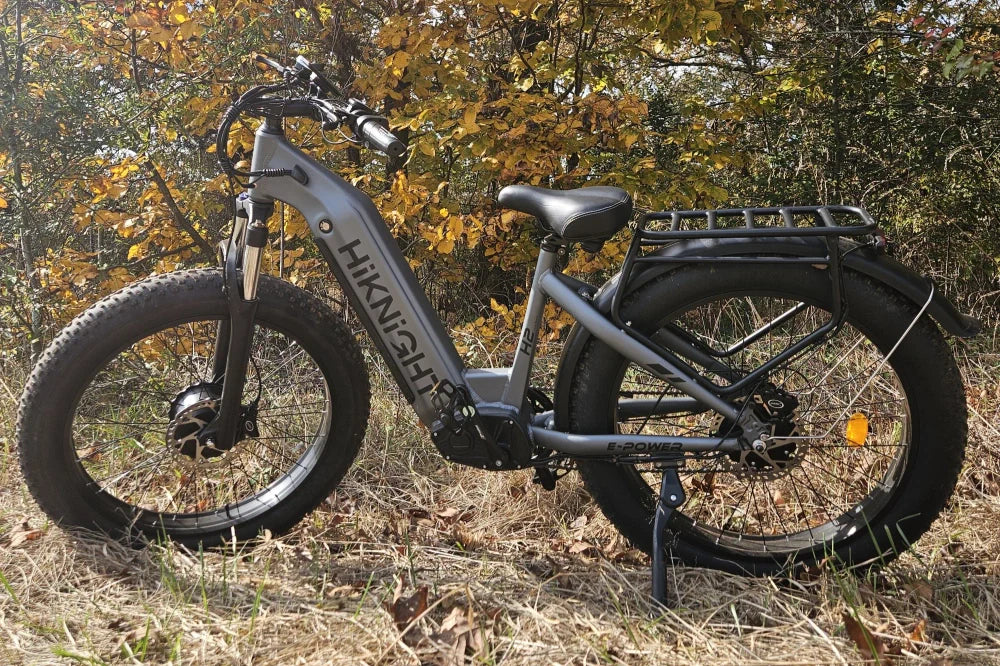
For riders seeking both versatility and power, fat tire designs within higher ebike classes offer strong advantages. The HiKNiGHT H2 dual motor fat tire electric bike shows how Class 3 capability can translate into everyday usability without sacrificing performance.
Ebike Class Laws and Regulations
Although ebike classes are widely recognized, local regulations still vary. Some regions restrict where Class 3 ebikes can be ridden or require helmets and age limits.
Checking local laws ensures your electric bike remains compliant and enjoyable to ride.
Final Thoughts on Ebike Classes
Ebike classes function as a practical performance guide rather than simple legal labels. By understanding how each class aligns with your riding style, you can choose an electric bike that feels purposeful and unrestricted.




















Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.